New Astrophotography Gadget
Over the years I've tried night sky astrophotography in several forms, never with great success. My accumulated collection of quality equipment never seemed enough to produce excellent results. I don't have a permanent observatory. It's getting physically harder to haul everything outside, set it all up, and tear it down afterward, especially in freezing conditions.
A small telescope, camera, filters, dew heater, and rechargeable battery are all contained inside this astounding device. It comes with its own tripod, and is controlled through a wifi connection to either a smart phone or tablet. The 50 mm telescope lens is visible in the next picture.
An image from the manufacturer's website shows the internal design.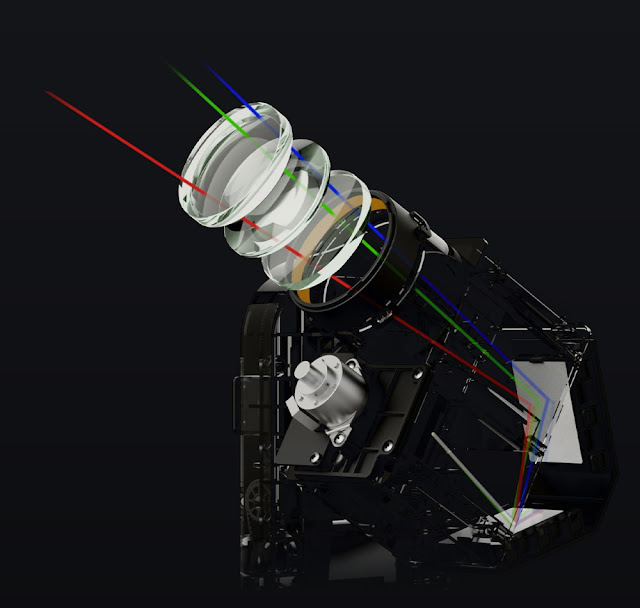
The whole thing is amazingly compact, just a bit larger than a cereal box.
It's also extremely portable because the telescope, tripod, solar filter, and USB cable fit within a small hard plastic carrying case.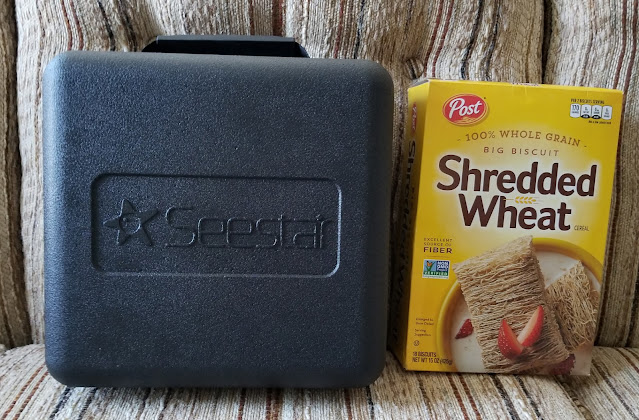
I took a couple Sun pictures
and one video. It was really easy to shut down and carry inside
when clouds increased minutes later, a welcome change from the effort and time needed
to break down and pack up my more complicated telescopic equipment. Clouds parted long enough to capture the quick Sun photo shown below (slightly sharpened using Registax wavelets). The image is good enough to show the whole Sun with
scattered sunspots. It isn't a high resolution
image capable of being magnified like images I get from my dedicated
solar telescope, but it's good enough to show some detail in larger sunspots.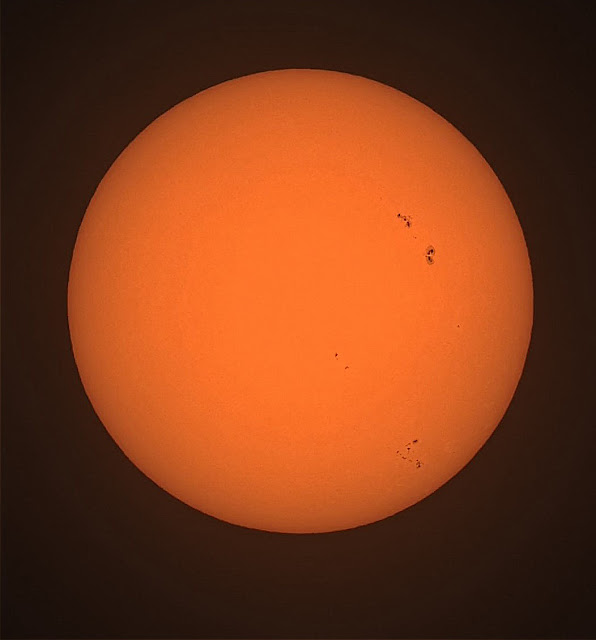
Clouds persisted into the evening of January 26th. Just
before going to bed I peeked outside and noticed significant gaps between clouds. I rushed
outside with the little scope. This time I used my tablet to control Seestar instead of my phone. The larger tablet screen was nice. It
was a pleasant warm 60 degree night. I sat comfortably
next to the scope and pointed it toward the full Moon. In no time I had
a couple nice snap shots of the Moon and one video. Conditions were about as poor as
possible for any other imaging. The full Moon was reflected from many scattered clouds and neighbor's spotlights were shining
directly into my backyard. This picture of the nearly full Moon was made by stacking 16 frames from a 161 frame AVI video.
Three days later, on January 29th, the evening sky finally cleared and the bright Moon did not rise until about 9:30. This was my first opportunity to use Seestar for long exposures of deep sky objects. In deep sky mode Seestar builds images by taking many consecutive ten-second exposures and automatically stacking (adding) them up to produce an equivalent single long exposure. My first target was the famous Horsehead Nebula in Orion. This dim nebula requires long exposure times. After a couple false starts I began to accumulate results. The image stack appeared to be building up as expected, but then it stopped getting brighter. Soon the telescope stopped imaging and told me the Horsehead's altitude had become too high for accurate tracking. I think images were being rejected from the stacking process because of tracking errors. So I switched to a much easier target, the famous Orion Nebula which has been imaged endless times by astrophotographers. I centered the nebula, commanded the internal light pollution filter to be inserted in the light path, and started accumulating 10-second exposures. During the subsequent half hour imaging time I went inside my house and monitored progress in comfortable interior warmth while the telescope continued working in the cold outside. The wifi connection was strong enough to allow telescope control from a distance! I could even watch TV while monitoring the image on my tablet! Thirty minutes later I had captured the image shown next.
Wow! The image above is better than any of my laborious previous attempts with other equipment!
Next I tried an object in the north, the galaxy pair M81/M82 in Ursa Major. Without going outside, I used my tablet to command the telescope to point to M81. It was extremely satisfying to see the preview image appear nearly centered on the tablet screen! Unfortunately, the galaxy pair was arrayed across the narrow side of Seestar's rectangular field of view, so both galaxies are near the edges. This is one of the disadvantages of Seestar. There's no way to rotate the field of view like I can when my Nikon is attached to my large refractor. At some other time of night the galaxies might be in another more favorable orientation within the field of view. I'll have to explore the possibilities in the future. I accumulated ten-second exposures for 20 minutes and produced the following image.
Eventually, the 88-percent illuminated gibbous Moon rose and Seestar's battery was getting low. It was time to stop long exposures. Before shutting down I pointed toward the rising Moon and took a 90-second AVI video. I then stacked 100 out of 1,000 video frames to produce the next lunar image.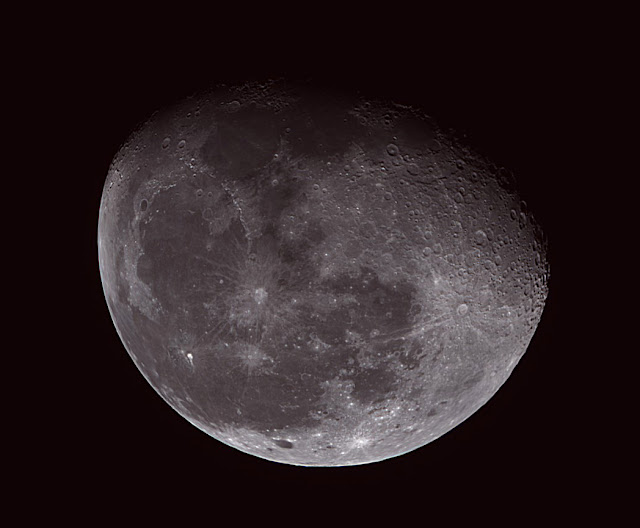
Seestar has some disadvantages. The telescope has a relatively small 50 mm aperture. The altitude/azimuth mount cannot track without incorporating unavoidable image rotation during long exposures. Tracking is difficult at high altitudes near the zenith. The field of view is small. Image quality will never match what is produced by larger, more expensive equipment. On the other hand, portability and wonderful ease of use are valuable compensating advantages. On cold nights when the effort to set up complicated equipment becomes an obstacle, Seestar overcomes the motivational obstacle. Requiring only one short trip outside, it can begin capturing images within about 15 minutes of startup. And it can be controlled wirelessly from within a comfortable house! I'm very happy with the Seestar system and looking forward to using it more!







No comments:
Post a Comment